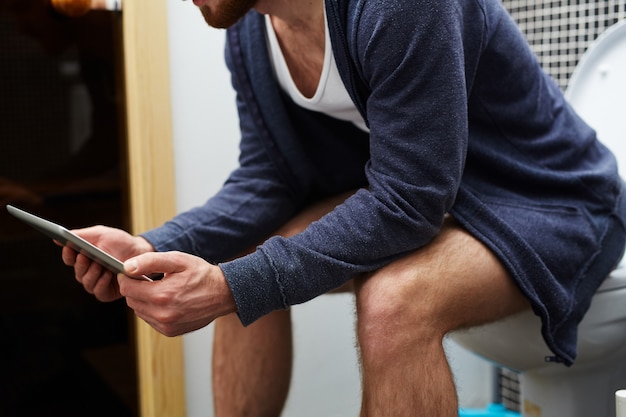
It’s a common habit: grabbing your smartphone the moment you sit on the toilet. Whether you’re catching up on social media, checking emails, or watching videos, bathroom time has become prime screen time for millions. But what seems like a harmless way to pass the minutes could be putting your health at risk. Recent research suggests that using smartphones on the toilet may significantly increase your chances of developing hemorrhoids—thanks to prolonged sitting and increased pressure in the rectal area.
A growing body of evidence points to a direct correlation between smartphone use in the bathroom and the development of hemorrhoids. According to a recent study, individuals who use their phones while on the toilet face a 46% higher risk of developing hemorrhoids compared to those who don’t. This risk persists even after adjusting for other contributing factors like diet, physical activity, and age.
The culprit isn’t the phone itself, but the behavior it encourages: extended sitting. The average bathroom visit lasts 5 to 10 minutes. However, smartphone users often spend 15, 20, or even 30 minutes on the toilet—time that adds up and increases pressure on the veins in the lower rectum.
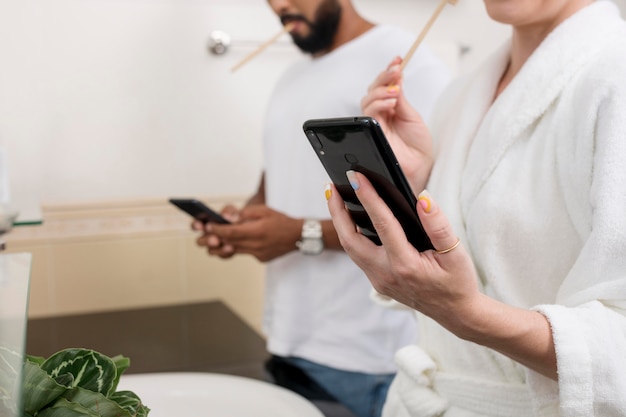

Prolonged toilet sitting due to smartphone use can increase rectal pressure.
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus and lower rectum, similar to varicose veins. They can develop internally (inside the rectum) or externally (around the anal opening) and often cause discomfort, itching, pain, and sometimes bleeding during bowel movements.
Sitting for long periods—especially on the toilet—increases pressure in the blood vessels of the pelvic and rectal areas. This pressure can cause the veins to swell and become inflamed over time. The toilet seat position, which places the body in a semi-squatting posture, naturally increases strain during bowel movements. Add a smartphone into the mix, and the duration of this strain multiplies.
Smartphones are designed to capture and hold attention. Infinite scrolling, notifications, and quick access to entertainment make it easy to lose track of time. A survey found that 66% of adults admit to using their phones while on the toilet. For many, this turns a quick bathroom break into a lengthy session.
This extended sitting doesn’t just affect hemorrhoid risk. It can also contribute to other issues such as:
The good news? You don’t have to give up your phone entirely—just change where and when you use it. Here are some effective strategies to reduce your risk:
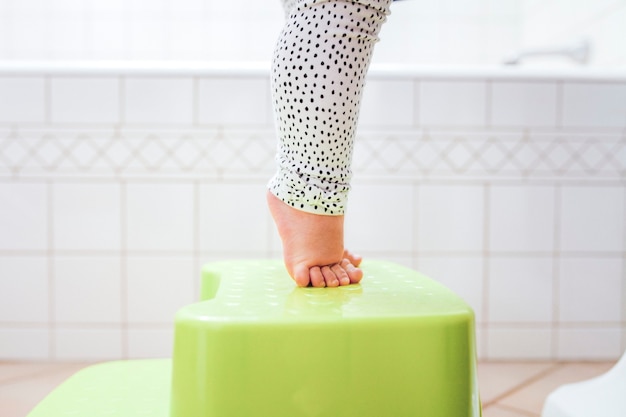

A footstool can improve posture and reduce strain during bowel movements.
If you experience persistent pain, itching, or bleeding during bowel movements, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. While most hemorrhoid cases can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments, some may require medical intervention.
Early action can prevent complications such as thrombosed hemorrhoids (clotted blood vessels) or chronic discomfort that affects daily life.
Smartphones have transformed nearly every aspect of modern life—including our bathroom habits. While it may seem convenient to scroll through your phone while on the toilet, the long-term consequences could include a painful and preventable condition like hemorrhoids.
By being mindful of how long you sit and making small changes to your routine, you can protect your digestive and rectal health. The next time you reach for your phone before heading to the bathroom, ask yourself: is that extra scroll worth the risk?
Your health starts with small choices—make them count.

Health

Health

Health

Health

Health

Health

Health

Health

Health

Health
Health

Health

Health

Fitness

Health

Health