When it comes to shedding fat while building lean muscle, diet plays a pivotal role—especially for men focused on fitness and body composition. Two of the most popular and well-researched eating plans are the low-carb diet and the Mediterranean diet. But which one is more effective for fat loss while supporting muscle gain?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll compare the low-carb and Mediterranean diets head-to-head, analyze their impact on fat burning, and help you choose the best path—whether you’re a beginner or an experienced lifter looking to optimize results.
Before diving into fat loss, let’s clarify what each diet entails.
A low-carb diet typically restricts carbohydrate intake to 20–150 grams per day, depending on the variation (e.g., ketogenic, Atkins, or moderate low-carb). The idea is to reduce insulin spikes, shift the body into fat-burning mode (ketosis in strict versions), and preserve muscle mass by increasing protein and healthy fats.
Common foods include lean meats, eggs, fish, non-starchy vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils—while avoiding bread, pasta, sugar, and most grains.
Rooted in the traditional eating habits of countries like Greece and Italy, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, olive oil, fish, and moderate dairy and wine. It’s rich in fiber, antioxidants, and heart-healthy fats—especially monounsaturated fats from olive oil.
Carbohydrates are not restricted but come from high-quality, unprocessed sources. Protein is moderate, with an emphasis on plant-based and seafood sources.
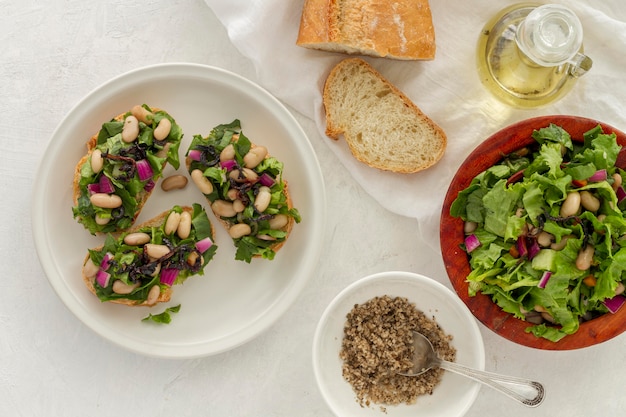

Multiple studies have compared low-carb and Mediterranean diets for weight and fat loss. Here’s what research shows:
For men aiming to build muscle, protein intake and energy availability are crucial. Here’s how the diets stack up:
Low-carb diets can support muscle gain if protein intake is high (1.6–2.2g per kg of body weight) and resistance training is consistent. However, very low carb intake may reduce workout intensity due to limited glycogen stores—especially during high-volume training.
While not traditionally marketed for bodybuilders, the Mediterranean diet can support muscle growth when combined with adequate protein (e.g., adding extra chicken, fish, or legumes) and strength training. The steady energy from complex carbs helps fuel intense workouts and recovery.

Regardless of which diet you choose, success comes down to three principles:
The answer depends on your goals, lifestyle, and preferences:
Both diets outperform the standard Western diet in fat loss and overall health. Neither requires calorie counting, but portion control and food quality remain essential.
For fast fat loss and appetite control, low-carb diets have the edge—especially in the first 3–6 months. But for lifelong health, flexibility, and balanced muscle growth, the Mediterranean diet is a powerhouse.
If you're a muscle-focused man aiming to burn fat, consider starting with a moderate low-carb approach to jumpstart results, then transitioning toward Mediterranean-style eating for long-term sustainability. Combine either plan with progressive resistance training, sufficient protein, and weekly tracking to maximize outcomes.
The best diet is the one you can stick to—while still building strength, losing fat, and feeling great.

Fitness

Fitness

Fitness

Fitness

Health

Health
Health

Health

Wellness

Wellness

Health

Fitness

Health

Fitness

Health

Health